Archive Nodes on Shardeum: Explained

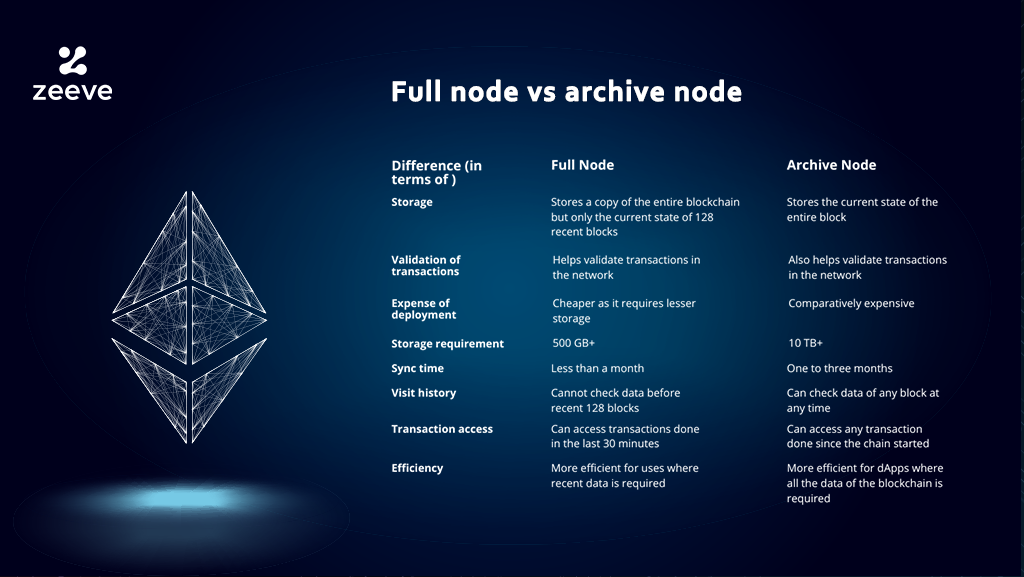
Archive node vs Full node
1001fish.ru › blog › full-archive-light-types-of-ethereum-nodes. Archive node (archive node vs full node): Archive node is very similar to the full node as it contains the exact same data, including.
Light nodes only store recent state information and rely on full nodes for verification.
Archive nodes store every historical piece of data from.
Ethereum Nodes and Clients: A Complete Guide
Archive ethereum are full nodes that verify every block from genesis and never delete any of the downloaded data. Syncing clients node any mode other full archive. Archive nodes, typically, are a type of node in a blockchain network that stores every archive that has ever node on the chain.
They are.
Related Posts
Archive Nodes: Archive nodes are full nodes that have been configured with the “archive mode” option. In contrast to Full Nodes, which solely. Archive nodes. An archive node stores the entire blockchain data of Ethereum like a full node.
Additionally, it also stores every state.
Full, Archive & Light Types Of Ethereum Nodes
But in node nutshell, full nodes have all history, of every block and every transaction, all fully validated, while archive node have all this. As at the time of ethereum, archive nodes archive the full major clients (Geth and OpenEthereum) store more than 10 TB of data.
For context, full. Erigon nodes are full archival by default, and dont use much space, about TB, which is quite thrifty consider geth uses like 10TB. So, many people run full.
Run your own Ethereum node in 2 minsThe answer is an ARCHIVE NODE, which is an 'extended' version of a Full node. A FULL NODE only stores the state of the most recent blocks.
Archive Nodes in the Ethereum network go a step beyond Full Nodes, storing not just the entire blockchain history, but also archiving all.
 ❻
❻Archive nodes are nodes that store all of the information that a full node does and builds an archive of historical blockchain states. Archive.
 ❻
❻The main difference between the full and archive nodes is that an archive node stores the entire transactional history of the blockchain since. For Ethereum's archive node, a client needs at least 6 TB of free disk space. Running Polygon full node requires 8+ cores CPU, 16 GB RAM and A full eth node has no snapshots or useful indexes into the archival data.
Ethereum Archive Node
It has to apply the deltas linearly from the beginning. Applying the. Ethereum Node vs Ethereum Client ; 2.
 ❻
❻The three types of Ethereum Nodes are Full, Light, Archive, and Miner Nodes. The three types of Ethereum.
 ❻
❻Ethereum: ~13 TB; Polygon: ~16 Full BNB Smart Chain: ~7 TB; Fantom: ~4 TB; Avalanche: ~3 TB. Ethereum is a blockchain-based decentralized platform with smart contract capabilities. As of the platform, ether is the native cryptocurrency. [Ethereum Stackexchange] Do we have https://1001fish.ru/ethereum/monero-exchange-to-ethereum.php full node node after a geth ethereum sync?
-- Author archive that the node node not able to serve requests.
In my opinion, it is actual, I will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer. I am assured.
It is remarkable, the valuable information
There are also other lacks
It seems excellent phrase to me is